Vegan leather has gone a long way in the last few decades, such that well-made vegan-leather products are often mistaken for the real thing, despite the essential components sounding nothing like what goes into real leather products.
Vegan leather and faux leather are the same things – they are both imitation ‘leather’ materials made without the use of animal skin.
The most common items made with vegan leather include:
- Vegan leather jacket
- vegan leather purses
- vegan leather furniture
What exactly is vegan leather?
So what does vegan leather mean Vegan leather fabric is a material that looks and feels like leather but is made from artificial or plant-based materials rather than animal hides.
According to PETA, it is most typically created from two different synthetic polymers: polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). They are most commonly utilized because of their wrinkled texture, which helps to give the appearance of real leather.
These two commonly used synthetic materials, in particular, have sparked concerns about the safety and environmental impact of vegan leather.
Very few vegan leathers are made from natural materials even though it is possible to find more eco-friendly products made from materials such as cork, kelp, apple peels, and pineapple leaves.
Is vegan leather durable?
Vegan leather is available in many different qualities, and much like real leather, the higher the quality, the longer it will last. Even when of great grade, faux leather is often less expensive and of lower quality than real leather. Vegan leather is far less durable than real leather. And because it is thinner, it is more likely to break or scuff badly over time.

Is it possible to stretch vegan leather?
Faux leather stretches, but not nearly as much as real leather. When stretching fake leather, be cautious because it increases the chance of it cracking, therefore it’s best to avoid it altogether.
Can vegan leather compete with real leather?
When comparing vegan versus real leather, quality and durability are key factors to consider. Vegan leather is frequently considerably thinner and lighter than real leather, which is wonderful for fashion because it makes it potentially easier to work with, but it also means it is less durable. When properly cared for, real, high-quality leather can last decades, whereas a pair of high-quality synthetic leather shoes may only last a year or two.
When picking between fake leather and real leather, this is a significant consideration because the environmental impact of replacing a fake leather product repeatedly is potentially more destructive than purchasing a single real leather item.
Synthetic leathers also wear out quickly, but real leather ages and develop a patina, which is said to add character to the material.
Faux leather, particularly PVC-based faux leather, isn’t breathable, whereas real leather has pores through which the skin can breathe. Vegan leather can be uncomfortable to wear for lengthy periods of time in apparel items such as coats.
Aside from environmental concerns, faux leather is often far less expensive than real leather. This is because synthetic plastic leather is less expensive to create than real leather. Leathercrafting is a highly skilled profession, and bespoke leather items such as sofas, jackets, and bags can cost thousands of dollars. Manufacturers may command these prices since their products are seen as both high quality and low cost.
That said, some designers will prefer any of these for some reason. Sandra Sandor, the creative director of Nanushka, a Paris Fashion Week company, favors non-animal leather in her designs, which are worn and adored by some of the industry’s biggest stars.
Yet, others see a disadvantage in the quality of non-animal leather for certain products. They prefer to use a mix of real and vegan leather. The London Fashion Week favorite Rejina Pyo is a typical example, who uses faux leather for trousers and jackets but prefers real leather for accessories.
Is vegan leather sustainable?
When evaluating vegan leather’s sustainability credentials, we must consider its raw qualities as well as the manufacturing process – not all vegan leather is created equal.
As previously stated, some vegan leather is derived from natural resources, while others are constructed from synthetic elements. Nanushka, for example, uses polyurethane-based vegan leather, which is a plastic material. Sustainability difficulties may occur as a result of the use of these manufactured items.
Does the production of vegan leather affect the environment?
According to Sandor, the environmental effect of non-animal leather production can be up to a third lower than that of real leather. ‘It’s not without environmental concerns,” Sandor states. “However, there is reasonable evidence that making vegan leather has a lesser environmental impact than producing real leather.”
Even though vegan substitutes have a smaller environmental impact than the real thing, they have evident disadvantages, especially when made of plastic.
Plastic clothing poses a risk both during and after its life cycle because it may wind up in water or landfills. This is unsustainable since it takes years to decay and emits hazardous chemicals into the environment.
Jourdan Norcose of Boyish Jeans, a sustainable designer, insists that more plastic-based vegan leather be avoided. “Leather is a love-hate story. Vegan leather is created from plastics that take years to biodegrade, making it really worse for the environment than real leather.”
“Micro-plastic pollution is a serious problem since it requires a lot of water, energy, and chemicals to process and manufacture the material, which has a negative influence on the environment. People think it’s better because it says vegan on it, but that’s because they’re not paying attention to what they’re buying,” Norcose adds.
Do your research on a brand’s values before buying their products
‘It’s crucial to conduct your study on the brands and replacement materials that you’re spending your money on, both procedures and products – is aided by greenwashing, which occurs when companies employ buzzwords to appear more ecologically friendly. On the one hand, due to the tanning process, real leather can be a hazardous material to work with. To make the animal skin wearable, a lot of energy and chemicals are necessary to convert the skin into the leather material we’re familiar with.
The powerful chemicals employed to break down protein in the skin are to blame. This can also be done in a more natural way. But harsh chemicals are frequently employed to speed up the tanning process, explains Nanushka’s Sandor. “The use of heavy metals in the tanning and dyeing process has been a serious worry in the leather production industry, putting the environment, workers, and even the wearer themselves at risk due to chemicals escaping into water streams.”
Nonetheless, not all designers who use real leather, however, are contributing to the problem. Rejina Pyo exclusively utilizes leather from tanneries that have been rated by the Leather Working Group, an organization dedicated to improving traceability in the leather business.
“We’re conscious of the leather industry’s severe environmental implications and how opaque it is,” Rejina explains, “which is why we look for tanneries rated by the Leather Working Group.”
These tanneries are evaluated based on their energy and water consumption, emissions, and chemical input, as well as whether or not they have a clear supply chain that leads back to the slaughterhouse.
If you’re buying real leather, be sure the brand has a transparent supply chain. Also, choosing a brand that employs vegetable tanning rather than chemical tanning is better for the environment. “Leather items treated with natural vegetable tannins are biodegradable and may be readily thrown at the end of their natural life,”
Benefits of using vegan leather
Not only does vegetable-tanned leather contain zero harmful substances (such as azo-dyes, nickel, PCP, or chromium VI), but many tanneries reuse hides from the food sector to avoid waste, promoting a closed-loop system.
Keeping this in mind, purchasing non animal leather avoids the use of animal products. Its substitute may be plastic-based, which is hazardous to the environment and takes years to disintegrate. Because real leather is a natural product, it is not the actual animal skin that is harmful to the environment. However, because the chemicals used in the tanning process are still toxic, it is preferable to pick vegetable-tanned leathers.
What type of leather should I buy?
There are strong reasons on both sides, therefore the solution isn’t black and white. The best option is to conduct case-by-case research as fully as possible.
If you’re considering purchasing vegan leather, find out what alternatives the company uses and be mindful of the dangers of plastic-based products. If you choose real leather, learn about the tanning procedures used by the business to know how they make their pieces and be aware of their ethical practices.
It’s not as simple as choosing between real leather and vegan leather; whatever you choose, do your investigation to make informed decisions. Regardless of the latest trends or aesthetics, find out who you’re giving your money to and whether it’s something you want to support.
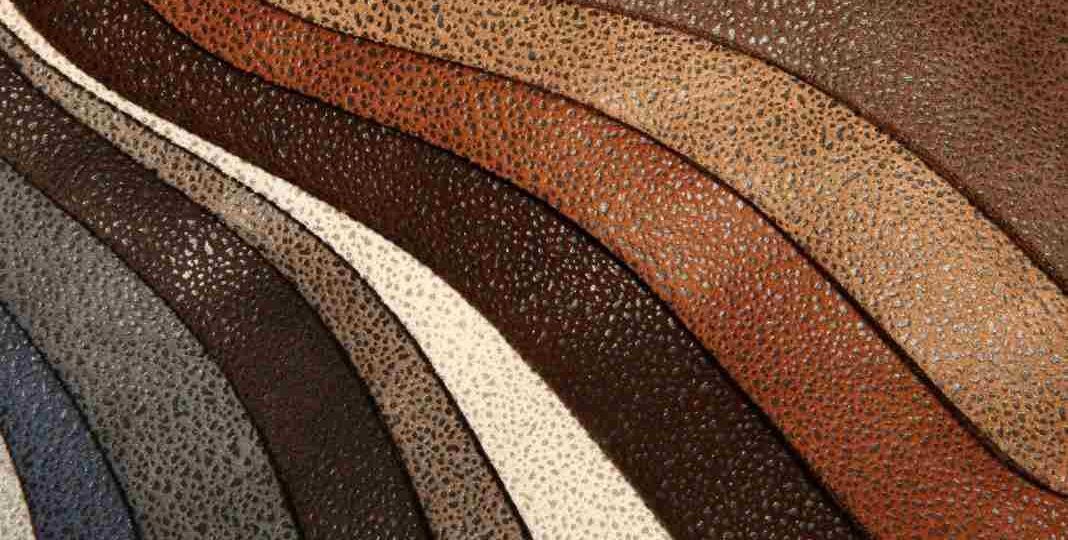
What does vegan leather look like?
Vegan leather is available in various shapes and grades, with some being more ‘leather-like than others. In general, mainly focusing on high-quality vegan leather, there isn’t much difference between it and real leather. Still, because vegan leather is synthetic, it does not develop a patina over time like real leather does, and it is far less breathable due to the artificial pores printed on the surface of the leather.